Photograph by DeAgostini/Getty Images
Written by Keketso Dibakwane and edited by Kamdi Okonjo
NOK Civilization
NOK Civilization
The Nok civilization, an ancient African people, flourished in the southern region of West Africa, encompassing present-day Nigeria, during the Iron Age, spanning from 500 B.C.E. to 200 B.C.E. Archaeological evidence suggests that the Nok culture emerged gradually and evolved in isolation. However, intriguingly, this once-thriving civilization vanished abruptly from historical records. The Nok civilization represents a significant population of the Iron Age, with evidence of their early use of iron for activities such as smelting and toolmaking dating back to approximately 550 BC, and possibly even earlier.
Image taken from Wikipedia
The Nok Civilization, considered the earliest identified form of Nigerian culture, offers valuable insights into the region's ancient history. While no evidence of activity exists for the first millennium BC, active trade routes connected Egypt, Nubia, the Sahara, the forest, and the Savanna people during the second millennium BC. The Savanna people acted as intermediaries, facilitating the exchange of various goods.
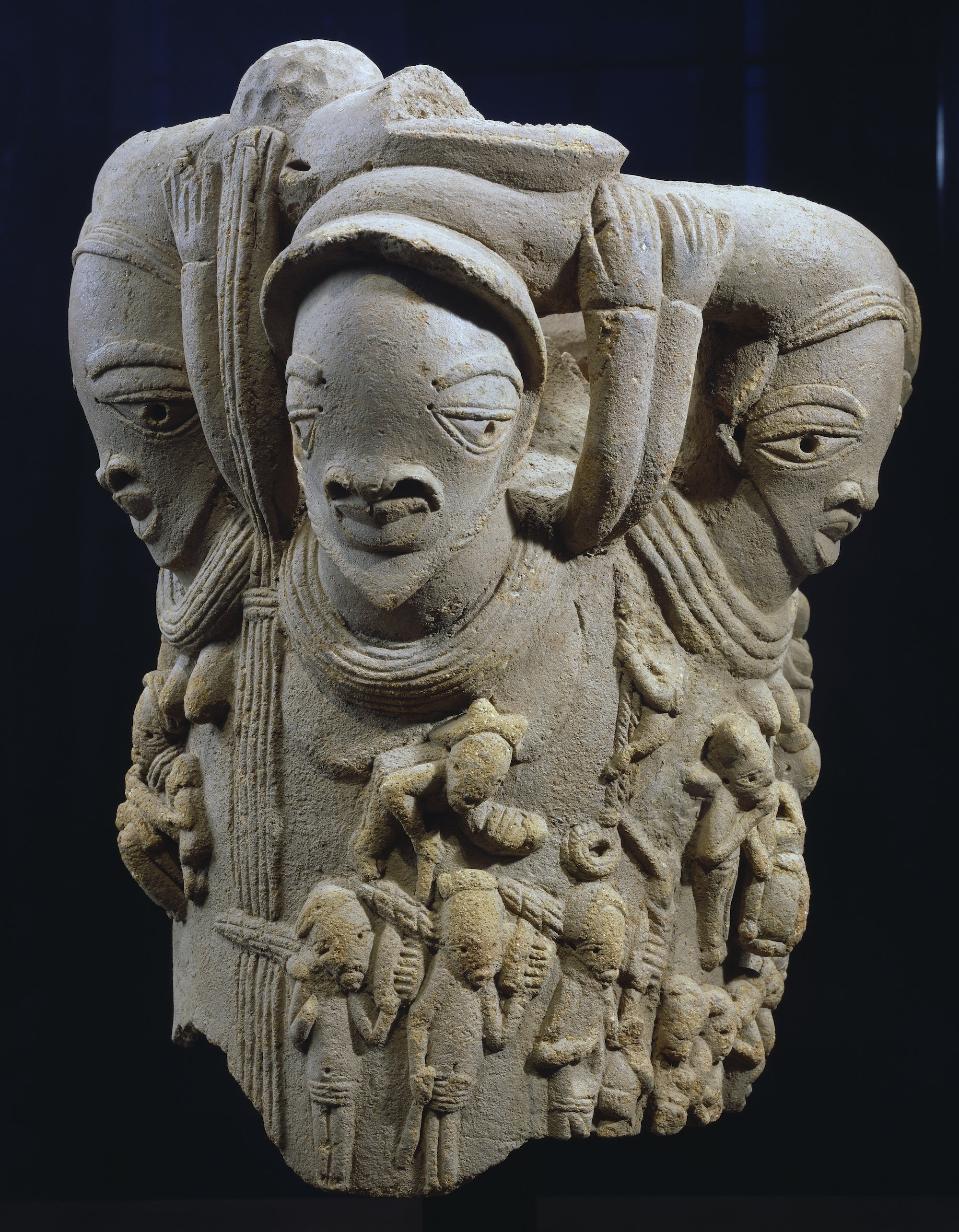
Archaeological discoveries form the primary basis for understanding the Nok Civilization. In 1943, Bernard Fagg embarked on a mission to collect and excavate fragments of clay shards and terracotta. Through careful dating of these fragments, he uncovered the existence of a western African society dating back to at least 500 AD. Fagg named this culture "Nok" after the village where the initial discovery took place. Subsequently, Fagg's research efforts yielded further artifacts, including sculptures, domestic pottery, stone axes, various tools, and iron implements.
These archaeological findings have provided crucial evidence for understanding the Nok Civilization, shedding light on their artistic expressions, technological advancements, and everyday lives. The discoveries made by Bernard Fagg and subsequent research efforts continue to deepen our understanding of this ancient Nigerian culture and its significance in the broader narrative of African history.
Nok Civilization Culture and Society
The Nok civilization was a complex and culturally rich society that displayed extraordinary skills for its time. As a sedentary community, the Nok people lived in one place rather than being nomadic. Primarily farmers, they formed a small yet thriving society. Despite their localized settlement, the impact of the Nok civilization extended far beyond their immediate surroundings. This is evidenced by the discovery of Nok Sculptures across an expansive area spanning approximately 78,000 square kilometers.
The Nok civilization gained global recognition for their remarkable terracotta art and iron age implements. The terracotta sculptures produced by the Nok people hold significant artistic value not only within Nigeria but also worldwide. These sculptures, predominantly in the form of hollow, coil-built human heads and bodies, exhibit highly stylized features, intricate jewelry, and diverse postures. They offer a glimpse into the artistic sophistication and aesthetic sensibilities of the Nok civilization.
Although the origin of their knowledge of ironworking remains uncertain, the Nok people were an iron age civilization that displayed mastery in smelting and forging iron tools. Whether they independently discovered ironworking techniques or acquired them through interaction with neighboring societies is yet to be determined. However, their adeptness in working with iron stands as a testament to their technological advancements and their ability to harness the transformative power of metal.
The artistic legacy of the Nok civilization, as showcased by their extraordinary terracotta sculptures, continues to captivate and inspire admirers worldwide. These ancient artifacts serve as a window into the rich cultural heritage and artistic achievements of the Nok people, leaving an indelible mark on the global artistic landscape.
“One of the identifying characteristics of Nok sculptures is the triangular or oval-shaped eyes on human faces. Human figures also often have elaborate hair styles. Typically, humans are depicted seated, with their hands on their knees.” National Geographic
A remarkable aspect of the Nok Culture was their proficiency in ironworking, which played a defining role in their civilization. Archaeological findings indicate that the Nok people had already embraced iron technology as early as the fourth century BCE. Their ability to smelt iron was a significant factor in the flourishing of their culture, enabling them to craft a wide range of iron tools.
The knowledge and practice of iron smelting revolutionized their society, allowing them to manufacture tools that greatly enhanced their daily lives. The mastery of ironworking granted them access to a diverse array of implements, such as agricultural tools, weapons, and other essential instruments. This technological advancement not only improved their efficiency in farming and hunting but also contributed to their overall socio-economic development.
The Nok people's skill in smelting iron reflected their inventiveness, resourcefulness, and capacity for innovation. The introduction of iron technology greatly influenced their culture, transforming their way of life and positioning them as a pioneering civilization in the region. The ability to produce iron tools was instrumental in the Nok people's success and played a significant role in their cultural, economic, and technological achievements.
“Nok culture provides the earliest example of iron-smelting technology in sub-Saharan Africa which may have come from Carthage to the north or, perhaps more likely given the formidable barrier of the Sahara desert, from Nubia in the east”. World History Encyclopedia
The purpose behind the creation of Nok sculptures remains a mystery, but archaeologists have drawn intriguing insights from their findings. The consistent use of clay from a single source in the production of these terracotta sculptures suggests the presence of a centralized state or possibly a complex hierarchical society within the Nok civilization. The sculptures, with their distinctive features and craftsmanship, offer clues about the social and cultural dynamics of the Nok people.
Some experts propose that the Ham people of southern Kaduna state were responsible for the development of the Nok culture and were once integral to the Nok civilization. This theory suggests a connection between the Ham people and the remarkable artistic achievements of the Nok civilization. Additionally, it is believed that the Nok culture may have influenced subsequent Nigerian cultures, most notably the Ife people. The Ife civilization, which thrived between the 11th and 15th centuries C.E., was renowned for its exquisite metalwork, suggesting a possible artistic and cultural continuum from the Nok culture to later Nigerian societies.
However, despite the wealth of archaeological discoveries, there is a scarcity of information regarding the Nok culture, its customs, and even its origins. The limited available records present a challenging puzzle for researchers, and many aspects of the Nok civilization remain enigmatic. Continued archaeological investigations and interdisciplinary research may shed further light on the Nok culture, unraveling its mysteries and enriching our understanding of this ancient African civilization.
Nok Civilization Location
The Nok civilization's exact location remains elusive to historians and archaeologists. The name "Nok" itself derives from the Ham village in Kaduna state, Nigeria, where the first terracotta sculptures associated with the civilization were unearthed. Ham village is situated in the northern region of Nigeria, specifically within Kaduna state.
Nigeria, officially known as the Republic of Nigeria, is a sovereign state located in West Africa. It is a diverse and culturally rich nation with a vibrant history that encompasses various ancient civilizations, including the enigmatic Nok culture. Nigeria shares borders with several countries, including Niger to the north, Chad to the northeast, Cameroon to the east, and Benin to the west.
As a West African country, Nigeria boasts a significant presence in the region and has played a crucial role in the cultural and historical tapestry of Africa. While the specific location of the Nok civilization remains uncertain, its impact on the understanding and appreciation of ancient African civilizations cannot be understated. The discoveries made in the vicinity of Ham village have shed light on the remarkable artistic and technological achievements of the Nok culture, leaving a lasting legacy in the annals of Nigerian and African history.
The Importance of Nok Civilization in Contemporary Times
Indeed, the scarcity of information about the Nok culture is regrettable. However, this gap allows us the freedom to imagine and visualize our own rendition of the Nok civilization, enabling us to envision the Africa we desire. While the loss of the Nok culture is a tragic aspect of Africa's history, it serves as a poignant reminder to the younger generation that the preservation of our rich cultural heritage lies in our hands.
As Steve Berry eloquently expresses, "A concerted effort to preserve heritage is a vital link to our cultural, educational, aesthetic, inspirational, and economic legacies. All of the things that quite literally make us who we are." These words resonate deeply, reminding us of the importance of understanding and embracing our origins in order to achieve personal and collective growth.
In today's world, where success is often measured by financial gains, educational accomplishments, and striving to be the best, we sometimes forget the fundamental significance of knowing our roots. The history, or rather the lack thereof, of the Nok culture should serve as inspiration for young people to delve into research about their own cultures and actively work towards their preservation.
By exploring and preserving our cultural heritage, we honor the legacy of those who came before us and forge a stronger connection to our identity. It empowers us to appreciate the diverse tapestry of African history and fosters a sense of pride in our unique cultural backgrounds. In cherishing and safeguarding our cultural heritage, we ensure that future generations will have the opportunity to learn, appreciate, and draw inspiration from the rich legacy of Africa's past.
References
C. Elliott. “The Nok people of Nigeria were smelters of iron but also agriculturalists. C. Elliott describes how the culture they founded may have a deep effect upon the ancient history of Africa”. 5 May 1967. Available at: https://www.historytoday.com/archive/nok-culture
Christopher Muscato. “The Nok: People & Culture”. Available at: https://study.com/academy/lesson/the-nok-people-culture.html
By Alistair Boddy-Evans. “Nok Culture”. September 01, 2018. Available at: https://www.thoughtco.com/what-was-the-nok-culture-44236
National Geographic. “The Nok Culture”. Available at: https://www.nationalgeographic.org/encyclopedia/nok-culture/
World History Encyclopedia. “Nok Culture”. Available at: https://www.worldhistory.org/Nok_Culture/